Key Features
Applications
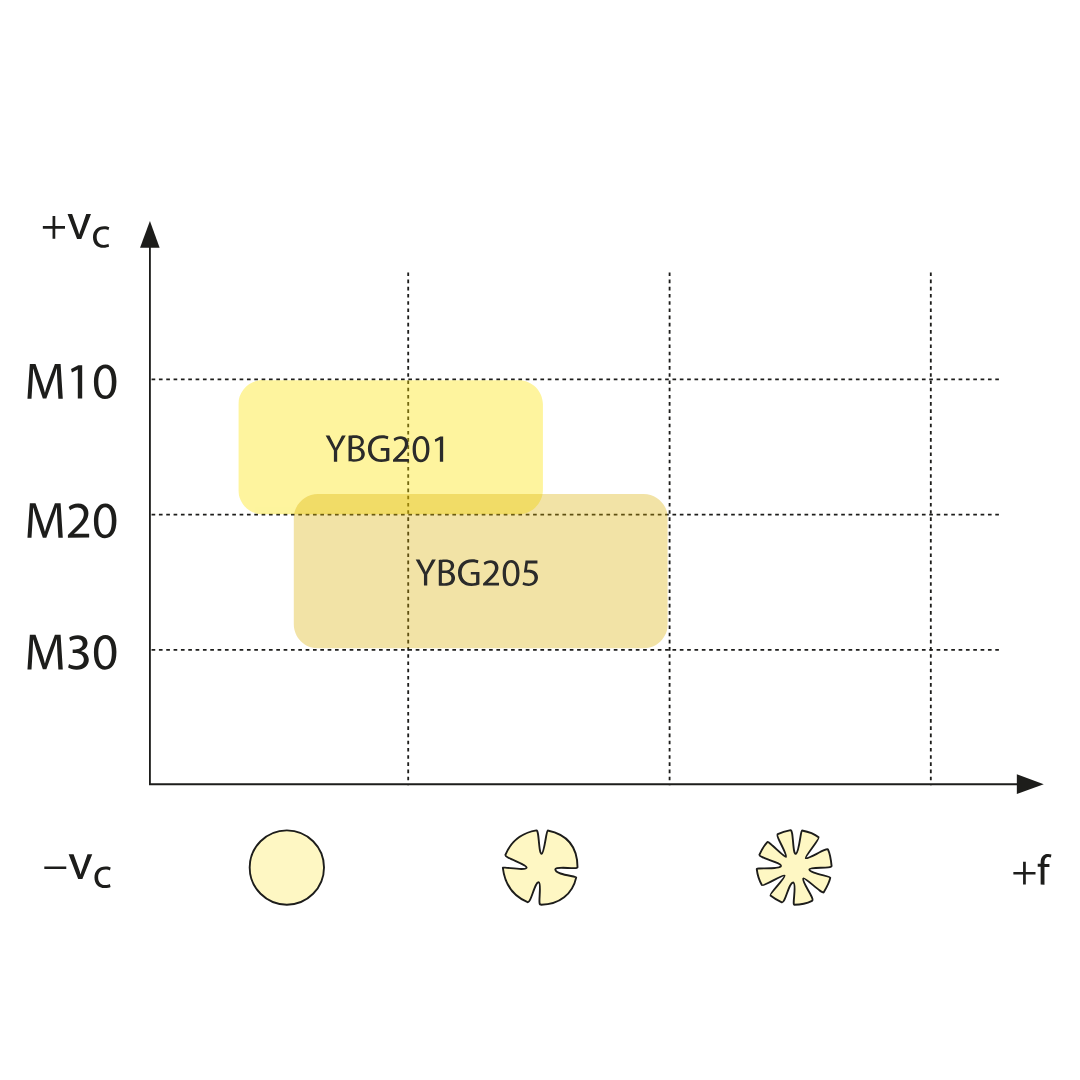
YBG201
ISO: P10 — P30, K10 — K25
PVD coated P10–P30/M10–M30 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application of steel and stainless steel. Good wear resistance in a wide application field.
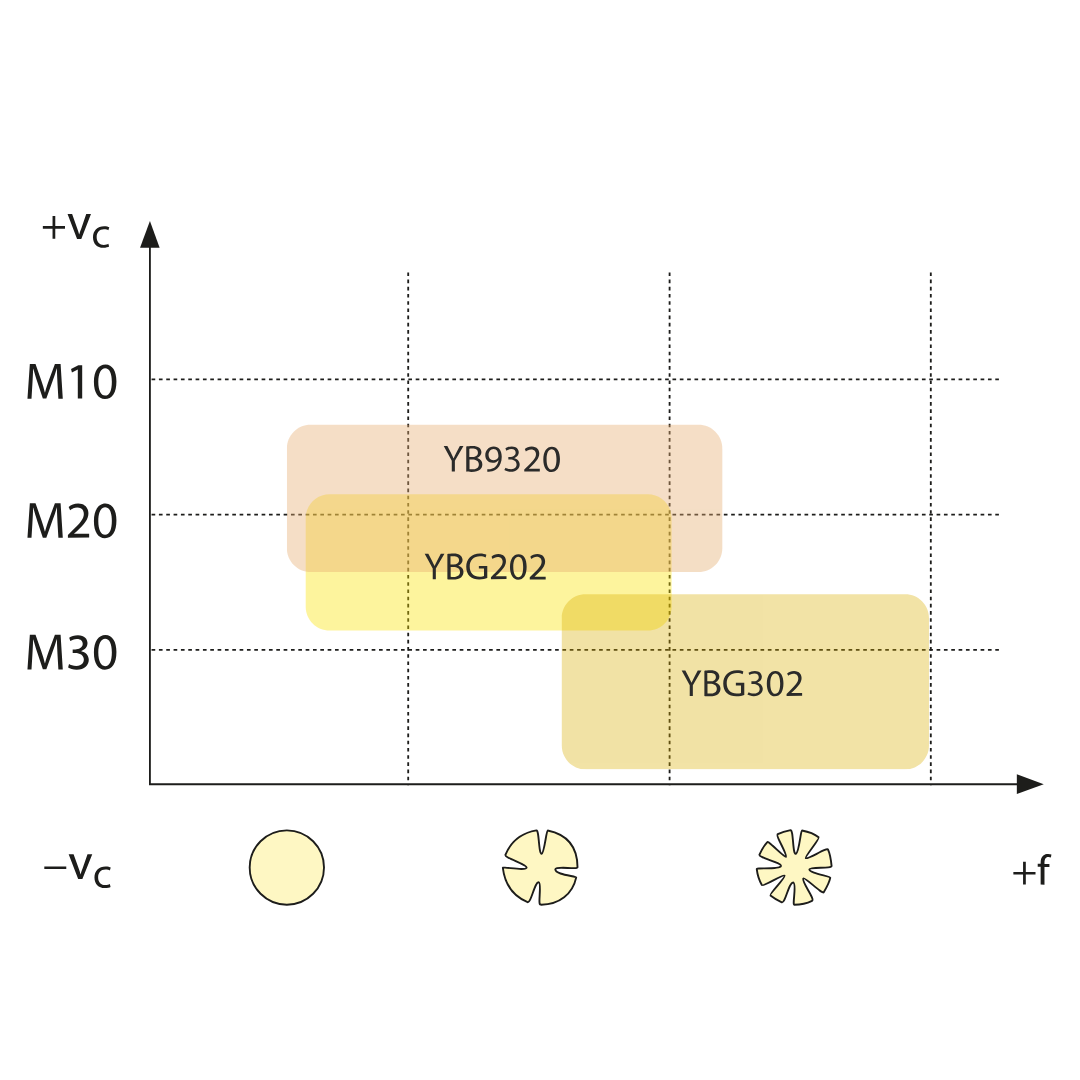
YBG302
ISO: P15 — P30, M25 — M40
PVD coated M25–M40/P15–P30 carbide substrate for medium roughing application of stainless steel and steel (milling). Good wear resistance and toughness.

YBG202
ISO: P10 — P30, M10 — M25
PVD coated M10–M25/P10–P30 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application of stainless steel and steel (milling). Good wear resistance in a wide application field.
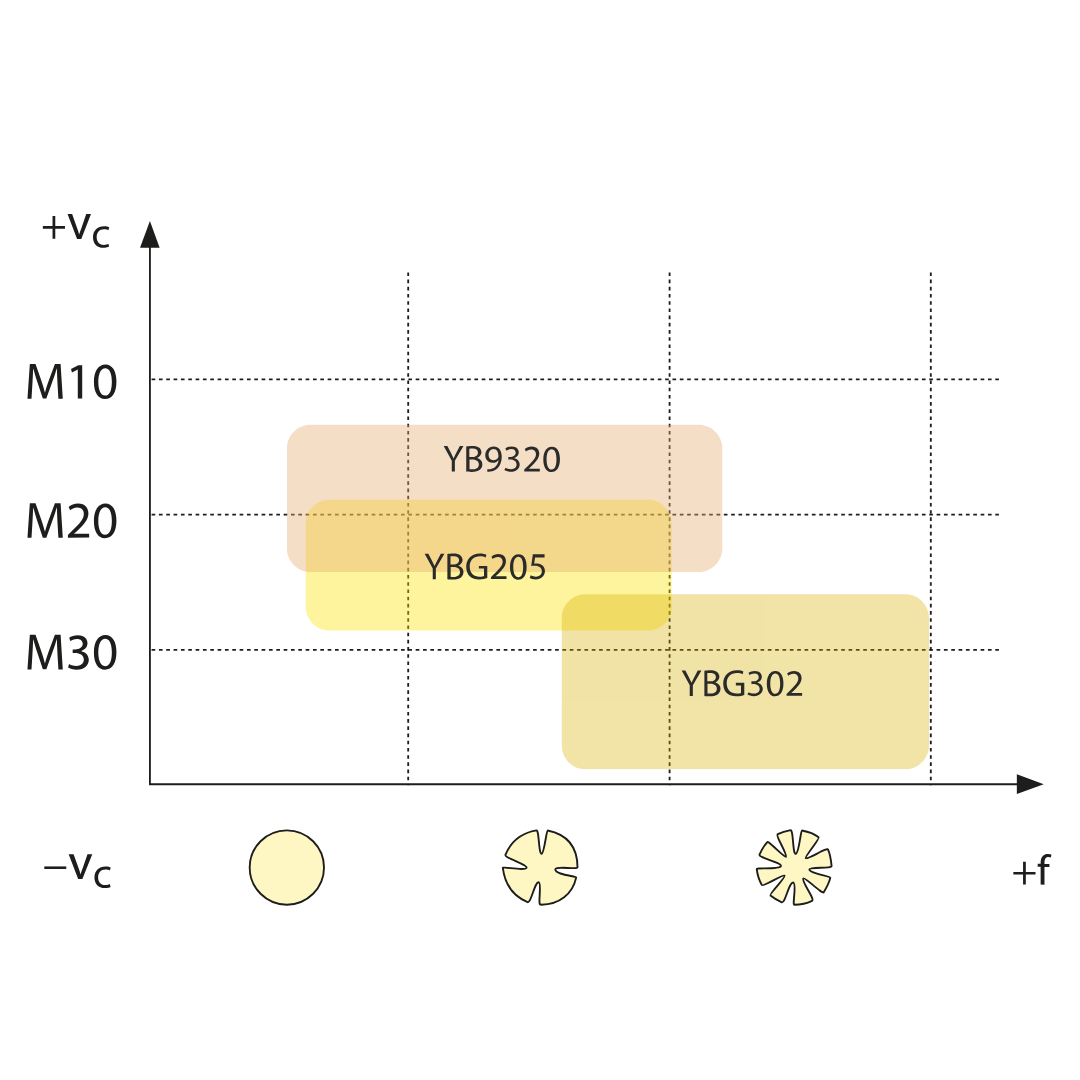
YBG205
ISO: P10 — P30, M20 — M40, S15 — S25
PVD coated M10–M25/P10–P30 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application of stainless steel and steel (milling). Good wear resistance in a wide application field.
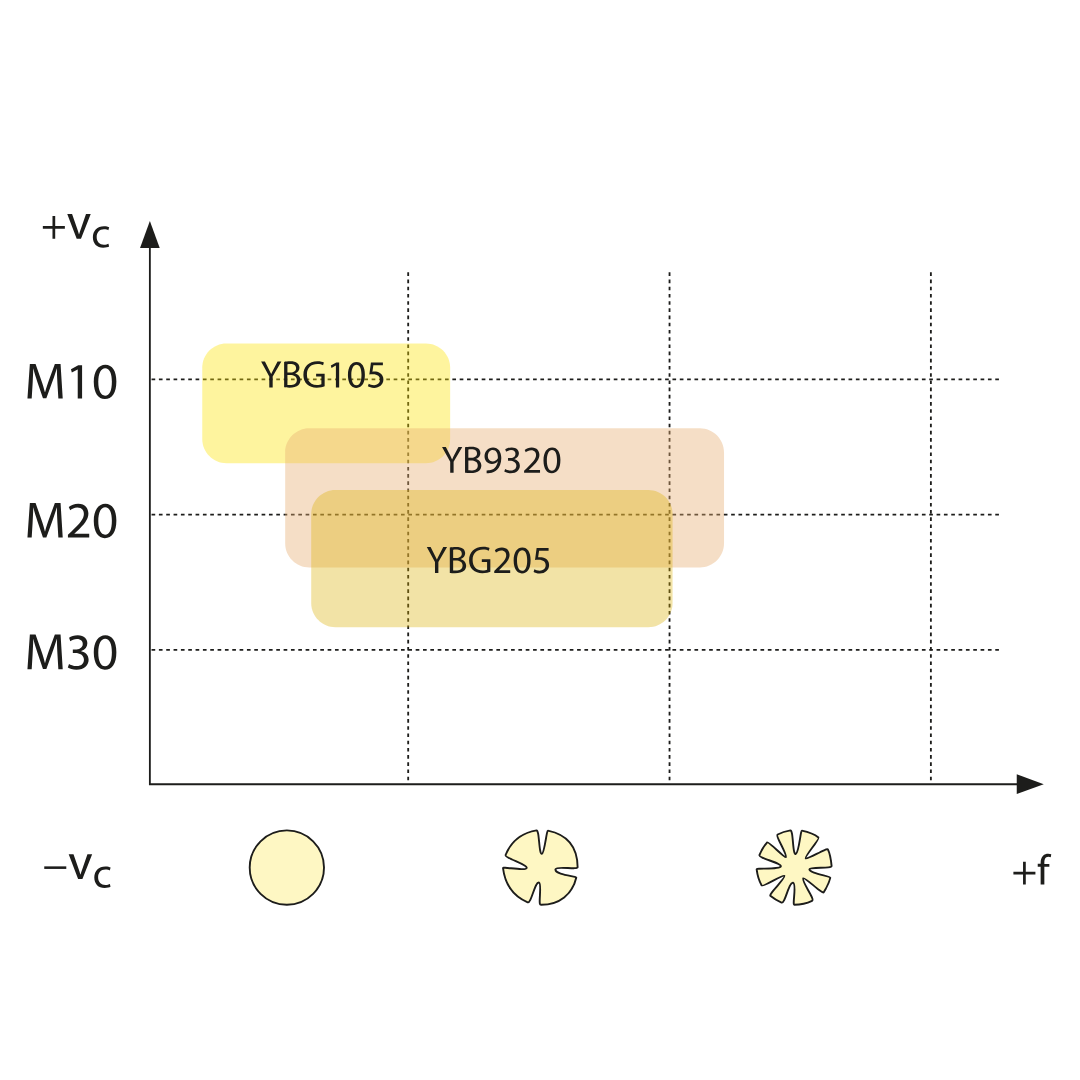
YB9320
ISO: P10 — P30, M10 — M25
PVD multilayer coated M10–M25/P10–P30 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application of stainless steel, super alloy and steel (grooving/milling). Optimized coating stability for higher wear resistance and thermal stability in a wide application field.
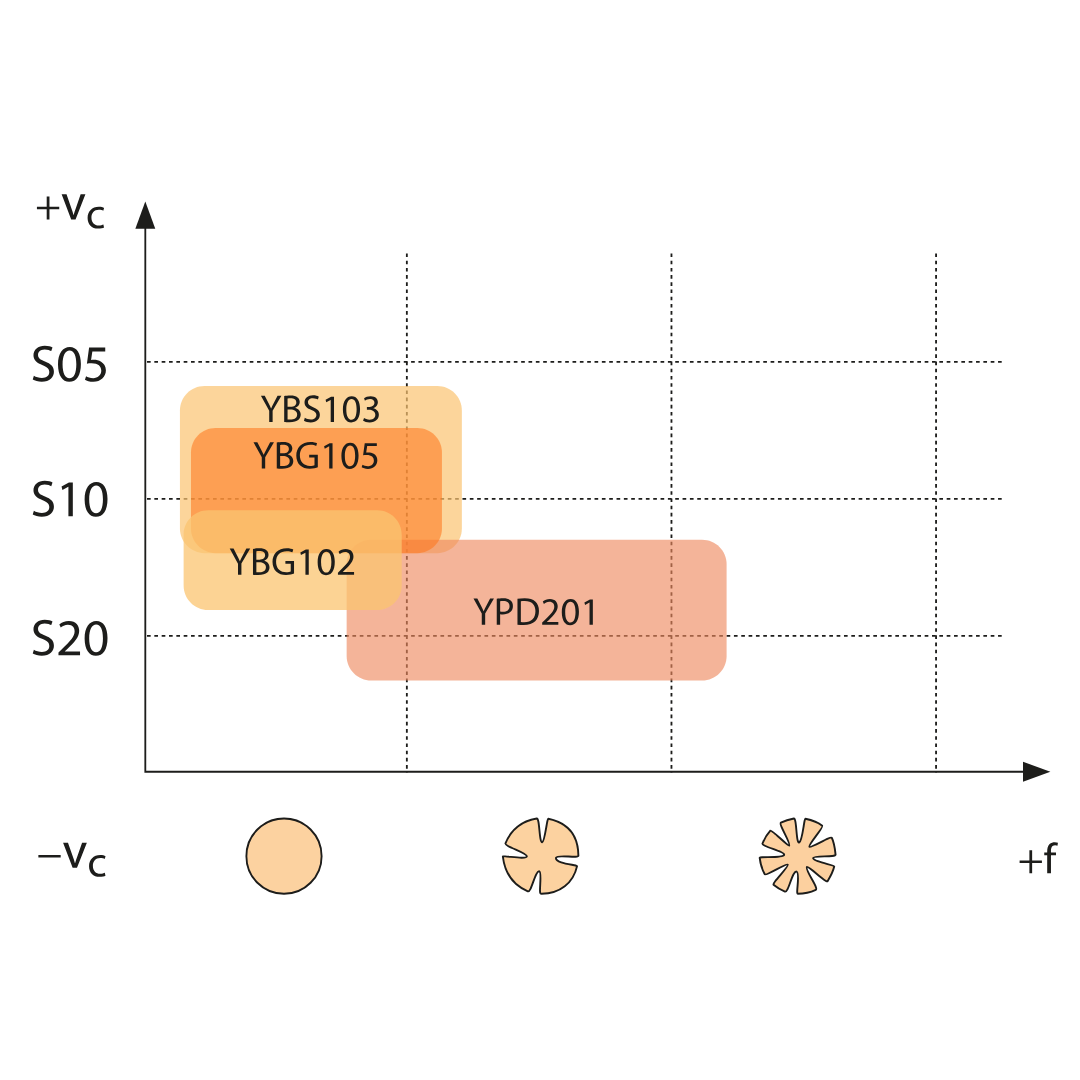
YBG102
ISO: S05 — S15
PVD coated S05–S15 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application of super alloy material, stainless steel and aluminium. Good wear resistance in a wide application field.

YBG105
ISO: S05 — S20
PVD multilayer coated S05–S20 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application of super alloy material but also stainless steel. Good wear resistance and thermal stability in a wide application field.

YBS103
ISO: S10 — S20
Turning grade for processing nickel-base materials. A special carbide substrate and the latest PVD coating technology enable a very good wear behaviour and high thermal stability.

YPD201
ISO: S20 — S30
Carbide grade for semi-roughing to chip breaking of high-strength and high-alloy materials. High-performance grade with high wear resistance. Balanced hardness and internal stress ratio provide a wide range of applications.
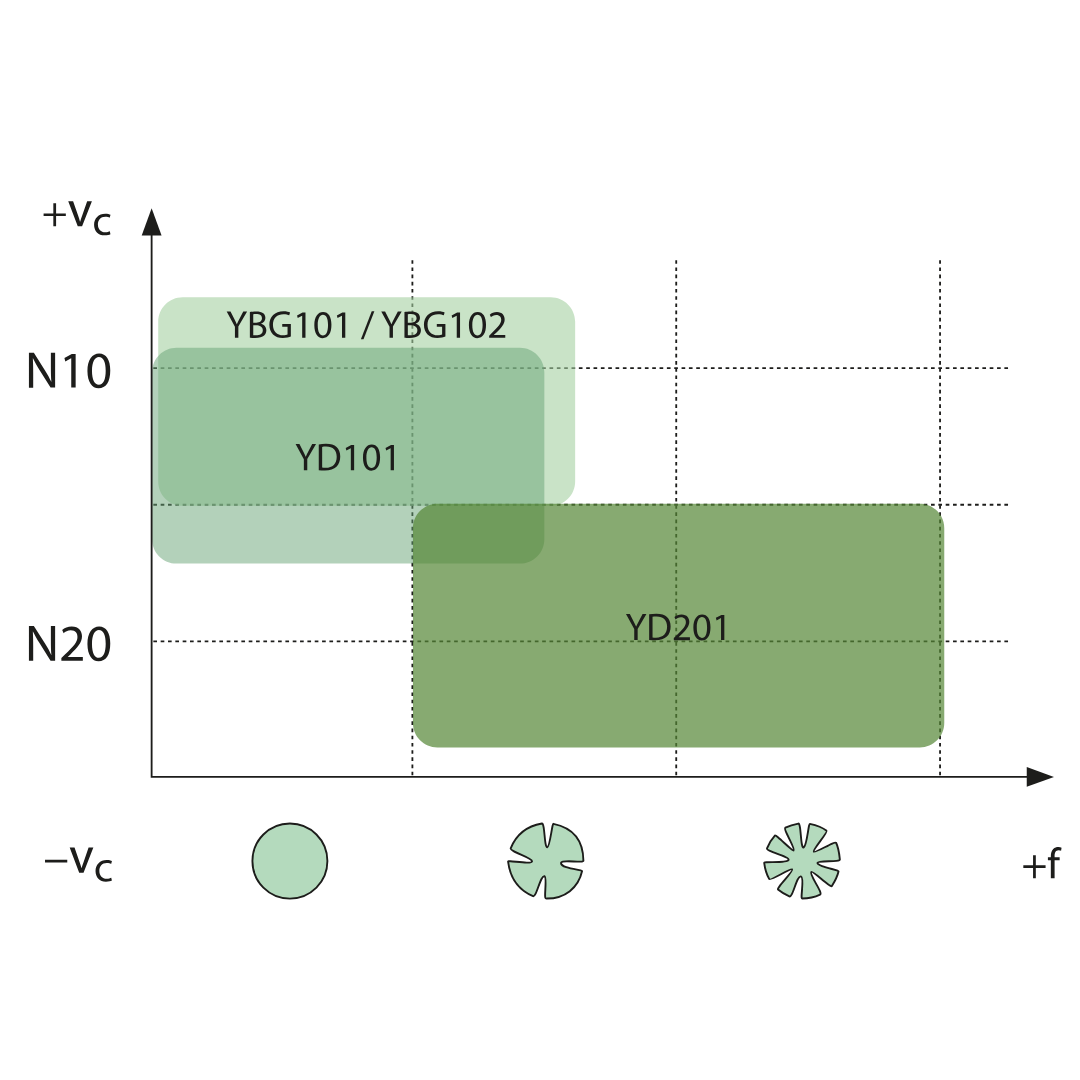
YBG101
ISO: N05 — N20
PVD coated N05–N20 carbide substrate for finishing to medium application in aluminium material. Coating only on the top face, in combination with the aluminium chip breaker, prevents build up edges and gives a smooth cut.

